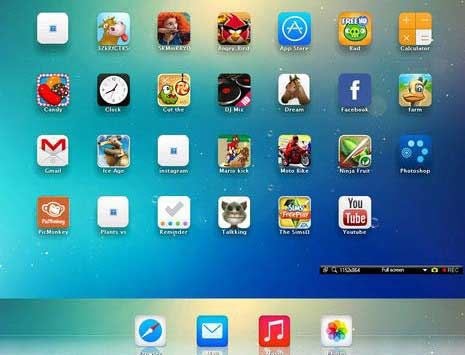
- Best Free Android Emulator
- Android Emulator Macos Bluetooth
- Emulator Android Macos Catalina
- Emulator Android Mac Os Download
Best Android Emulators for Mac to use Android Apps on Mac
Android is one of the most popular mobile platforms out there that is being used by millions of people from across the globe. No matter what kind of app you need, you can certainly find that for your Android mobile. Android is popular because of several reasons. First, the mobiles are very cheap and comparatively cheaper than iOS. Second, loads of free apps and games are available for Android on Google Play Store and third party stores. And so on. But, what if you want to install and use Android apps on Mac? Here are some best Android emulators for Mac so that you can install Android apps and games on Mac.
Setup Android Emulator on Mac OS X. The purpose of this section is to guide you to create in your development environment an Android emulator. Android emulators are managed through a UI called AVD Manager. AVD Manager has a nice interface when started from Android Studio. Start Android Studio app, then create a blank project. Mac OS, on the other hand, is a wonderful operating system used by Apple Inc. On it's Mac PC and MacBook. It has a marvelous user interface and great features. It will be fantastic if we were able to use Android apps on Mac PC. Luckily, it is possible by using an emulator. In this article, we will learn about the five best Android Emulators for. But the good thing is that just like Windows, macOS also got few best emulators that can run Android apps and games on the big screen. So, in this article, we are going to share some of the best Android emulators for MacOS. With these emulators, you can easily run Android apps and games on the big screen. Sep 24, 2021 Use the Android Emulator to test AR scenarios without a physical device. The Android Emulator lets you run ARCore apps in a virtual environment with an emulated device that you control. Set up your development environment. Software requirements: Android Studio 3.1 or later. Android Emulator 27.2.9 or later. Get Android Studio and SDK tools for.
Best Android Emulators for Mac to use Android Apps on Mac
There are several Android emulators for Windows. However, Mac users need to be careful before installing an Android emulator. Otherwise, you will end up installing bloatware eon your MacBook or iMac.
1] Bluestacks (Free)
Bluestacks is a very popular Android emulator for Windows. However, the same app can let you use Android apps and games on Mac as well. There is no need to head over to another Android emulator when you have it on your OS X machine. Bluestacks can assist you to install apps from APK files. That means if you have downloaded the APK file of app or game of Android, you can install that on your Mac through Bluestacks. Apart from that, tons of free apps and games are available inside the Bluestacks app. This is also possible to stream videos from Twitch, which is generally unavailable in other Android emulators for Mac. The best part is Bluestacks does support instant messaging clients. Which means you can talk to your friends over that IM even when you are using Mac. Download
Best Free Android Emulator
2] Manymo (Paid)
Not only Mac, but also you can use this Android emulator on any operating system since it works online. In other words, there is no need to install any third-party software or emulator to use Android apps on Mac. Manymo works as a browser based tool or web tool. However, you need to create an account. The setback is there is no free trial or free version available for this app. You must have to spend at least $9/month to get started with Manymo. The best part of this tool is you can select the Android version that you want to launch. For example, you wish to check how your app looks on an Android 2.3.3 mobile or Android 4.2 mobile. All those things can be done with the help of Manymo. Having said that, Manymo is pretty sloer than Bluestacks. Visit Webste.
3] Genymotion (Paid)
Genymotion is probably the best Android emulator for Mac. This does almost 95% job of a standard Android mobile. In other words, you can install apps, develop and test, change battery level to check performance of an app, use webcam as camera, and so on. Like Manymo, you can get all the versions of Android and 40 different kinds of Android devices so that you can test your app completely. Genymotion integrates with several other development kits such as Android Studio, Android SDK, and more others. Some useful sensors such as accelerometer, gyroscope, etc. are also available. Like an Android mobile, you can capture screenshots too. Genymotion costs around $136/year. The Business edition is priced at $412/year. Visit website.
There are more other free and paid Android emulators for Android. However, when it comes with development, you should opt for Genymotion. Otherwise, Bluestacks is the best fit for you.
This article is part of a three-part series on cross-browser testing Windows, iOS, and Android from macOS.
If you want to test your websites on an Android device, one option is to use an Android emulator to open a browser and navigate to your website. Android Studio, the official IDE of Android, ships with a built in emulator similar to the one we used in our previous post on cross-browser testing on iOS devices from macOS.

Note: This article was written using the following operating system and software versions:
– macOS Catalina, Version 10.15.7 on a MacBook Pro (Retina, 15-inch, Early 2013)
– Android Studio 4.1.0
To get started download Android Studio for Mac and install the application.
After launching the application, you’ll be asked to set the emulator settings if your system can run the emulator in an accelerated performance mode. I like to bump up the RAM allocation slightly to at least 4 GB.
Once Android Studio is installed, you don’t actually need to create or run a project to run the emulator. At the home screen, you can select AVD Manager from the Configure Menu in the bottom right.
From this menu, you should see at least one emulator, with a green start button to run it, as well as a button to Create new emulator.
From here you can start any existing Virtual Devices that are already available to you by clicking the green play icon. After launching the device you will see it boot up on your screen, and eventually will be taken to the devices home screen.
With the emulator running, you can now access your websites running on the host machine’s localhost, on 10.0.2.2. For example, if you have a NextJS app running on http://localhost:3000, you would be able to access that on the emulator on http://10.0.2.2:3000.
From the Android Virtual Device Manager screen, click “Create Virtual Device” to bring up the Virtual Device Configuration Screen. You’ll see a number of virtual hardware devices to choose from, select one and click next.
From there, you’ll be required to select the operating system you want to install. If you don’t have the system image already available, you’ll need to download it by clicking the Download button.
Download and walk through the component installer.
Once downloaded, you’ll be asked to give your Android Virtual Device a name and can set a few more options like the default orientation. Click finish to finalize the virtual device configuration.
You should now see the newly created AVD in the Android Virtual Device Manager.
Android Emulator Macos Bluetooth
Click the green play icon to launch your newly created AVD.
Once you’ve created some Android Virutal Devices in the steps above, you may decide to launch them from the command line to save time in your workflow. In the examples below we’ll be using iTerm2, but you can use any terminal application.
First, enter the preferences by navigating to Android Studio > Preferences, and then Appearance & Behavior > System Settings > Android SDK.
From this menu we are looking for the “Android SDK Location”. Copy the location and head over to your terminal.
The emulator executable is located in the “emulator” folder and is also named “emulator”. So in my case, I want the full path to the emulator to look like:
For ease of use, we’re going to alias this in our bash_profile so we don’t need the entire path and can just type “emulator” into the command line.

Now, you can use the command emulator -list-avds to see which emulators are available to you.
Now that we have the emulator command aliased, and we can view a list of emulators. We can easily launch new emulators by running emulator -avd [EMULATOR]. For example:
Debugging with the Chrome Web Inspector
Emulator Android Macos Catalina
If you want to take your AVD testing and debugging a step further, you can connect it to your desktop version of Chrome and debug using the Chrome Developer Tools.
In order to do this, you must first run the Android Debug Bridge (“adb”) from the command line.
To use ADB, first ensure you have the Android SDK Platform-Tools installed. You can find this information from the Android SDK > SDK Tools menu of the Android Studio preferences.
The adb program will be in the Android SDK location under the platform-tools directory. In my case it would be found at:
Just like the editor, we’re going to alias this in our bash_profile so we don’t need the entire path and can just type “adb” into the command line.
Now you should be able to run adb in the terminal and see the program help screen. With the virtual device running, run adb devices, which will start the bridge if it’s not already running and print any devices found with their status. If its set up properly, you should see an emulator with “device” next to it.
Launch Chrome on the virtual device, and also on your host machine. On your host, navigate to chrome://inspect/#devices. You should see the emulator and an option to open a new tab from the list.
You can either open tabs on the device itself, or type the name of your host in the text input and click open. Remember your host machine localhost will be 10.0.2.2 on the AVD.
Emulator Android Mac Os Download
Any tabs found on the AVD will show up under the device, and you can open the Chrome Developer Tools by clicking the “inspect” link. From there, a familiar Chrome DevTools window will be available and should be connected to the browser on the Android Virtual Device.